Most teams think they have “CRM + call center integration” because agents can click a phone icon inside Salesforce, HubSpot, or Zendesk. In reality, that’s step one. A true integration means every call is routed based on CRM context, every outcome is logged in the right place, recordings and QA scores are tied to accounts and tickets, and leaders can trust a single revenue story across systems. This checklist breaks that down into 37 concrete features you can tick off, grouped by routing, logging, recording, QA, analytics, and governance so you don’t discover gaps only after you’ve scaled.
1. Why CRM + Call Center Integration Is No Longer Optional
Customers don’t care which system owns their data; they just expect you to know who they are, why they’re calling, and what happened last time. If CRM and telephony are disconnected, you get repeated questions, misrouted calls, and incomplete history. When they’re tightly integrated, your call center stops being a cost line and starts acting like a revenue engine that prevents churn, similar to the outcomes mapped in modern cloud contact centre designs.
At a systems level, integration is about three things: real-time context for agents, complete post-call data for operations, and reliable signals for AI and forecasting. Without that, every new channel (WhatsApp, chat, email, voice) adds chaos instead of clarity. The rest of this checklist is built to help you audit where you stand today and design a roadmap toward the same integrated foundations that power advanced call center software stacks.
2. Architecture: How Data Should Flow Between CRM and Telephony
A healthy architecture keeps clear ownership boundaries. Your cloud telephony or contact center platform owns calls, queues, recordings, and raw metrics. CRM owns customers, leads, opportunities, and consent. Helpdesk owns tickets and SLAs. Integration connects them with event-based data flows instead of nightly CSVs, using patterns similar to those used in high-value call center integration catalogs.
In practice, that means: the call platform publishes events (ringing, answered, wrap-up, recording stored); the integration layer translates them into CRM-friendly objects; and CRM responds with context such as account status, segment, or open deals. When that loop is tight, screen pops feel instant, routing respects customer value, and AI has clean, labelled data to work with. When it’s loose, agents wait, screens don’t match callers, and analytics never fully tie back to revenue.
3. Routing & Experience: Features 1–10
Routing is where CRM data turns into real customer experience. Ten non-negotiable features:
- Contextual screen pop: inbound calls automatically open the right CRM record based on phone or account ID.
- Click-to-call everywhere: agents dial from any CRM list, record, or view with activities auto-logged, like in VOIP + CRM integration benchmarks.
- Skills-based routing from CRM fields: language, tier, or plan from CRM map to queues and skills.
- Priority routing for key segments: VIPs, high-ARR accounts, or at-risk customers skip generic queues.
- Campaign-aware outbound lists: dialer pulls leads from CRM views or reports, not static spreadsheets.
- Real-time eligibility checks: consent and DNC status in CRM enforced before any outbound call, aligned with compliant dialer setups.
- Case-aware routing: open tickets in CRM or helpdesk steer callers to specialist queues.
- Regional and language routing: country, region, and preferred language fields shape paths through IVR.
- Callback orchestration: callbacks triggered from CRM are scheduled and executed by the dialer with context.
- Blended routing across channels: calls, chats, and emails for the same account can be treated as one conversation.
These features ensure that “integration” shows up in the way calls land, not just in how they are reported. Without them, you might technically connect CRM and telephony but still feel like you’re running two separate operations.
4. Logging & Data Quality: Features 11–18
Call centers sink or swim on the reliability of their data. Eight more features define whether your logs are usable:
- Automatic activity logging: every call creates a CRM activity with date, duration, direction, and owner.
- Standardised dispositions: a governed list of outcomes syncs from telephony to CRM, enabling the kind of clean reporting used in metric-heavy call centers.
- Multi-object association: single calls can link to a contact, account, deal, and ticket when needed.
- Outcome-driven workflows: specific dispositions trigger CRM workflows, tasks, or pipeline stage changes.
- Duplicate prevention: phone-based matching rules stop integration from creating parallel records.
- Auto-tagging of reasons and topics: call reasons captured once, synced into CRM fields and reports.
- Fail-safe offline logging: if CRM is down, calls buffer and sync when it returns, rather than vanishing.
- Bi-directional status sync: key fields (like “Contactable” or “VIP”) update telephony in near real-time.
When this layer is weak, leaders start building parallel spreadsheets, QA struggles to find the right calls, and AI summarization tools have to work twice as hard to make sense of messy histories. When it’s strong, you can confidently push into more advanced setups, as seen in large integration roadmaps.
5. Recording, QA & Compliance: Features 19–27
Recording and QA are where legal risk, coaching, and trust in quality converge. Nine must-haves here:
- Recording links in CRM: each call activity contains a direct link to the call recording in your platform.
- Role-based access controls: only authorised roles can play, download, or share recordings.
- Configurable retention policies: retention by region, segment, or product line to match regulations.
- Automatic QA sampling: pre-defined percentages of calls land in QA queues per team or queue.
- QA score sync: scores and coaching notes write back to CRM or performance tools.
- AI-assisted QA: AI scores 100% of calls, with humans focusing on edge cases, similar to AI-first QA approaches.
- Redaction and PCI handling: payment and sensitive data automatically muted or excluded from storage.
- Consent and announcement rules: IVR and scripts align with regional requirements for recording notification.
- Audit trails: every access to recordings and QA results is logged for compliance teams.
Without this bundle, even the best CRM integration can leave you exposed in regulated markets or unable to prove quality to enterprise buyers. With it, you can speak confidently about governance during RFPs, backed by platforms built for low-risk migration like those in CIO survival guides.
6. Analytics, AI & Automation: Features 28–34
Once routing, logging, and QA are stable, analytics and AI turn the integrated stack into a decision engine:
- Unified reporting schema: a shared definition of “call,” “contact,” and “conversation” across tools.
- Attribution-ready events: calls tied to campaigns, opportunities, or subscription changes in CRM.
- Journey analytics: ability to see paths across IVR, agents, and channels, supported by telephony built for SIP-to-AI evolution.
- Real-time dashboards: CRM and BI dashboards that update within minutes of call activity.
- AI summaries into CRM: post-call AI notes attached to records so humans don’t re-write outcomes.
- Next-best action guidance: AI suggestions based on CRM stage, segment, and recent interactions.
- Workload automation: tasks, follow-ups, and sequences triggered without manual clicks, similar in spirit to AI-powered dialing engines.
These features are where integrated stacks generate their ROI. They compress admin, sharpen forecasts, and help leadership see which plays genuinely work rather than arguing over disconnected reports.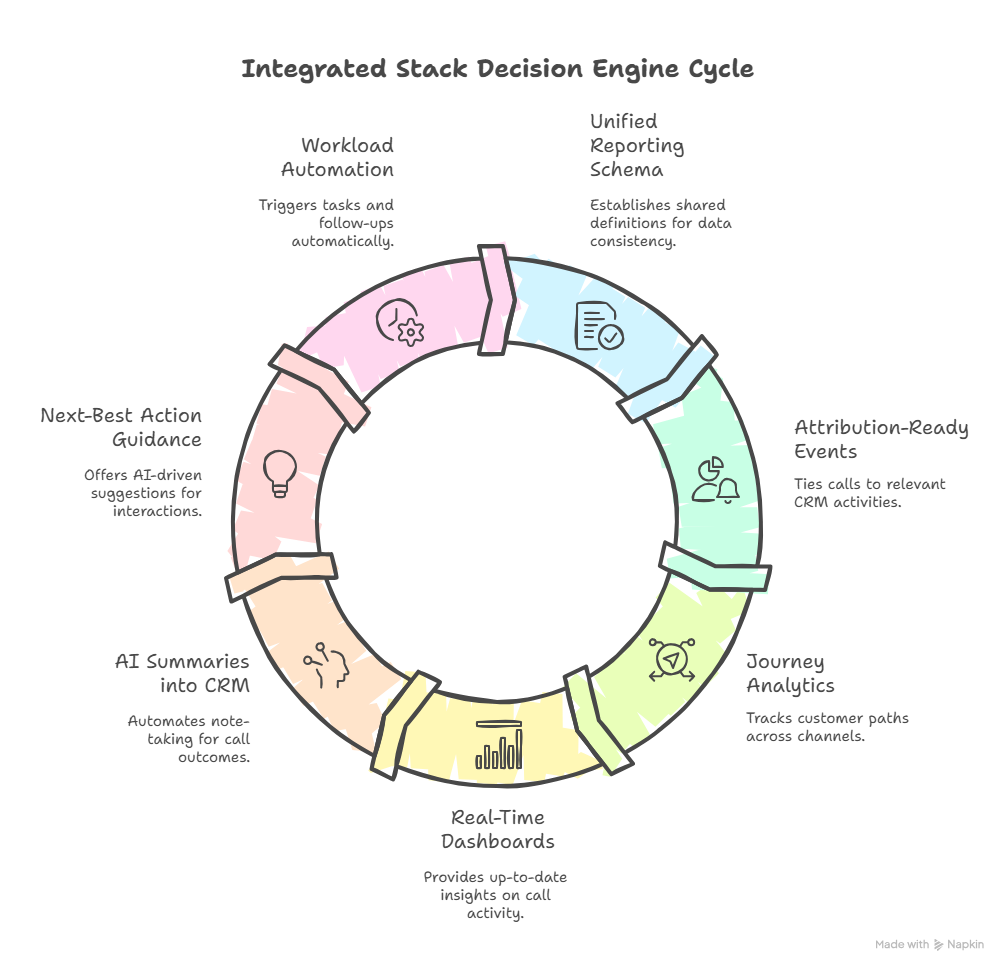
7. Governance & Change Management: Features 35–37
The last three items look boring but decide whether your integration survives the next year of growth:
- Integration owner and roadmap: one accountable owner with a backlog, not a “set and forget” project.
- Versioned configuration: documented mappings, fields, and flows so you can safely change or rollback.
- Structured change process: requests for new queues, fields, or workflows go through impact review before going live, just as careful as low-downtime PBX migrations.
Many stalled operations have decent technical integrations but no governance. Over time, ad-hoc changes pile up and the only fix is a painful clean-up project. A lightweight but enforced governance layer keeps that from happening.
8. 37-Feature CRM + Call Center Checklist (Snapshot Table)
Use this table as a single-page audit. If you can’t confidently tick a feature as “Done” or “In progress,” mark it as a gap to investigate.
| # | Feature | Category | Why It Matters | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Contextual screen pop | Routing | Cuts handle time and reduces repeated questions. | ⬜ |
| 2 | Click-to-call from CRM | Routing | Increases dials; keeps reps inside CRM views. | ⬜ |
| 3 | Skills-based routing from fields | Routing | Matches customers with the best-suited agents. | ⬜ |
| 4 | Priority routing for VIPs | Routing | Protects high-value accounts and reduces churn. | ⬜ |
| 5 | Campaign-aware dialer lists | Routing | Aligns outbound with marketing and sales motions. | ⬜ |
| 6 | Real-time consent enforcement | Routing | Prevents illegal or unwanted outbound calls. | ⬜ |
| 7 | Case- and ticket-aware routing | Routing | Speeds up resolution for open or escalated issues. | ⬜ |
| 8 | Regional/language queues | Routing | Improves CX in multilingual and multi-country setups. | ⬜ |
| 9 | Callback integration | Routing | Reduces abandonment and peaks on busy lines. | ⬜ |
| 10 | Omnichannel contact handling | Routing | Prevents fragmented experiences across channels. | ⬜ |
| 11 | Automatic call activity creation | Logging | Eliminates manual logging and missing calls. | ⬜ |
| 12 | Standardised dispositions | Logging | Enables clean reporting and forecasting. | ⬜ |
| 13 | Multi-object call associations | Logging | Connects calls to accounts, deals, and tickets at once. | ⬜ |
| 14 | Outcome-driven workflows | Logging | Automates follow-ups based on call result. | ⬜ |
| 15 | Duplicate prevention rules | Logging | Keeps CRM contact lists clean and usable. | ⬜ |
| 16 | Auto-tagged reasons/topics | Logging | Makes demand, issue, or churn reasons visible. | ⬜ |
| 17 | Offline logging resilience | Logging | Protects call history when CRM is briefly unavailable. | ⬜ |
| 18 | Bi-directional status sync | Logging | Aligns “contactable” or segment states across tools. | ⬜ |
| 19 | Recording links in CRM | Recording/QA | Gives easy access for leaders and coaches. | ⬜ |
| 20 | Role-based recording access | Recording/QA | Prevents misuse of sensitive recordings. | ⬜ |
| 21 | Configurable retention policies | Recording/QA | Aligns storage with legal and client requirements. | ⬜ |
| 22 | Automatic QA sampling | Recording/QA | Ensures consistent quality coverage per queue. | ⬜ |
| 23 | QA score sync to CRM | Recording/QA | Links performance with accounts and deals. | ⬜ |
| 24 | AI-scored calls at scale | Recording/QA | Covers 100% of calls instead of small samples. | ⬜ |
| 25 | Redaction/PCI-aware flows | Recording/QA | Keeps sensitive data out of recordings and logs. | ⬜ |
| 26 | Consent and announcement logic | Recording/QA | Aligns recording with local regulations and expectations. | ⬜ |
| 27 | Recording access audit trails | Recording/QA | Supports investigations and compliance audits. | ⬜ |
| 28 | Unified reporting schema | Analytics/AI | Stops teams from arguing over mismatched numbers. | ⬜ |
| 29 | Attribution-ready event design | Analytics/AI | Connects calls directly to revenue and churn. | ⬜ |
| 30 | Journey analytics capability | Analytics/AI | Shows which paths resolve or frustrate customers. | ⬜ |
| 31 | Real-time dashboards | Analytics/AI | Lets leaders react within hours, not weeks. | ⬜ |
| 32 | AI summaries into records | Analytics/AI | Saves time and raises data quality for every call. | ⬜ |
| 33 | Next-best action guidance | Analytics/AI | Gives agents prompts that align with strategy. | ⬜ |
| 34 | Workflow automation hooks | Analytics/AI | Triggers tasks and sequences automatically. | ⬜ |
| 35 | Named integration owner | Governance | Stops integration from becoming “everyone’s job, nobody’s job.” | ⬜ |
| 36 | Versioned configuration docs | Governance | Makes changes safe and reversible. | ⬜ |
| 37 | Structured change process | Governance | Prevents “quick tweaks” from breaking live queues. | ⬜ |
9. Implementation Roadmap: From Audit to Integrated Stack
A practical path starts with an audit session. Map where each of the 37 features sits today: “live,” “partial,” or “missing.” Then cluster work into three streams: routing, data quality, and analytics. Routing changes improve CX and efficiency fastest, especially when combined with the predictive or progressive dialer strategies described in dialer comparison frameworks.
Next, harden logging and QA. Standardise dispositions, tighten recording access, and turn on AI QA pilots for a few queues, borrowing ideas from AI cost-cutting toolkits. Finally, rebuild your dashboards on top of the new, clean data model. That might mean new CRM reports, a BI layer, or both. Each change should be piloted with one team or region first, then scaled once metrics and feedback confirm the design is solid.